Learning phonics reading is the first step in a child’s primary education and linguistic skills. Referring to how sounds are represented through various written letters, they help in understanding how words are formed.
Phonics teaches kids to take education beyond the written medium. By linking sounds with graphic symbols that represent them, learning phonics-based reading aids language development in young children.

Therefore, learning about phonics can be useful when you wish to learn any language. To learn a language from the basics, you have to master how certain letters sound on their own, and when they are used together.
Learning phonics-based reading is also one of the most common elementary skills kids pick up at school, that increases linguistic aptitude in children.
This article will therefore tell you all about phonics, how to learn to read with them, and their types. You can also find the best tips to imbibe phonics reading and master it at any age.
The Alphabetic Principle and Stages of Phonics Reading
An alphabetical principle is a relationship between written symbols and spoken sounds that helps us understand how a certain word is pronounced when written. The alphabetic principle and phonics are the same thing, as you must have guessed by now.
Phonics forms an essential part of reading and has five basic steps, according to the National Reading Panel. These steps are-
Phonemic Awareness
Refers to a person’s ability to mould syllables in order to form coherent words. Phonemic awareness through reading aloud helps children develop their linguistic profile in more than one-way instruction.
A phoneme is the smallest unit that denotes a sound. You can practice your phonemes with the following chart. Focus on how you say them because phonemes in one word might not be the same as in other words.
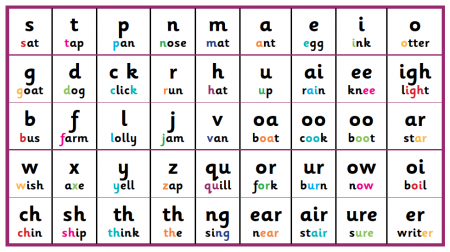
The other part of phonemic awareness is graphemes which are symbols that represent phonemes. Therefore, in order to form words and read them, phonemic awareness is of premier importance.
Saying a word out loud and writing it down can help children develop basic phonemic awareness. Reading syllables aloud is called decoding, and putting together letters that denote the sounds is called encoding.
Blending
The second step in learning to read these phonemes and graphemes to form legible and coherent words is called blending. This task is an advanced step and several children find it difficult to achieve this stage. Blending is one of the primary steps toward achieving fluency in spoken and written language.
Mastering Consonant and Vowel Clusters
It is here that children learn the difference between consonants and vowels. At the beginning, children pick up simpler words that have a CVC (Consonant-Vowel-Consonant) composition such as three-letter words like big, toy, man, pan, tip, etc.

The next stage is to move towards more complex words with CCVC or CVCC words that demand more expertise and a strong grasp of the basic principles of word formation and the sounds produced.
It is at this stage that we introduce children to vowel digraphs. A vowel digraph is when a word uses two vowel sounds in succession. For example- boat, float, deer, their, etc. Later, they move on to combine vowel digraphs with consonant clusters, forming more complex words. Children may also pick up consonant diagraphs alongside vowels.
Learning How to Spell
Spelling is an important part of phonics-reading that makes use of encoding to write down graphemes for the phonemes. Phonics establishes a familiarity between the two and enables children to make more words by adding suffixes and prefixes. From digraphs, students also learn to move on to trigraphs which use three vowels or three consonants in a word.
Fluency and Comprehension
The last stage of phonics-based reading is the achievement of fluency and comprehension abilities that help children make sense of what is being said, what is being written, and how to express themselves in a lucid, coherent fashion.
The most important fact about phonics is to teach children how to read correctly and grasp the meaning of different words. Phonics is not the same as picture-based instruction- substituting the latter for the former is one of the biggest elementary mistakes curriculums, teachers and parents have been making for a long time.
Teaching children to make sense of an image does not mean that they can understand what the written words imply. For example- if a child is shown a picture of a tabby cat and a wildcat before teaching them the specific words used for each animal, the child will be more likely to call both ‘cats’ rather than calling them exactly what they are.
A superficial sense of imagery does not equate to precise, correct information and can have a detrimental effect on how children comprehend a given word or an image whenever they encounter it.
When Should You Teach Your Child to Learn Phonics Reading?
Phonics can yield the best effects if taught at the earliest. Teaching children how to associate words with sounds lays a strong foundation for cognitive development. It is important to administer phonics instruction to children even before they begin school.
A solid example of how phonics can be taught to children is how Anne Sullivan taught the blind, deaf and mute Helen Keller to grasp the meaning of the word water. Sullivan poured water on her pupil’s hand while spelling it on her other hand. While this is not exactly phonics-based reading, Sullivan could help her pupil learn the meaning of words as well as how they were to be written.
There is no limit to how should you be teaching phonics to your kids. However, it is important to help them develop a strong affinity for written and spoken language that will help them later in life through effective methods.
Types of Phonics
There are three different kinds of phonics. Sometimes, people believe that there are four types. However, the fourth category is a sub-type of the main category. We have laid it down for you below with examples-
Analytic
When students are taught to analyze letter-sound connections previously taught to them so as they do not break those sounds while pronouncing them.
Embedded
This implicit approach is when students are taught how to embed sounds while reading the text.
Synthetic
When children learn to blend graphemes in phonemes and blend them to form words.
Special Mention- Analogy
Analogy phonics are a subset of analytical phonics where students learn to associate a certain cluster with words.For example- the words knickers, kick, brick, truck have the -ck cluster in common.

